Gamer’s Thumb: Prevention and Relief Console gamers
Key points
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor. Esports Healthcare disclaims any liability for the decisions you make based on this information.
The information contained on this website does not establish, nor does it imply, doctor-patient relationship. Esports Healthcare does not offer this information for diagnostic purposes. A diagnosis must not be assumed based on the information provided.
What is gamer’s thumb?
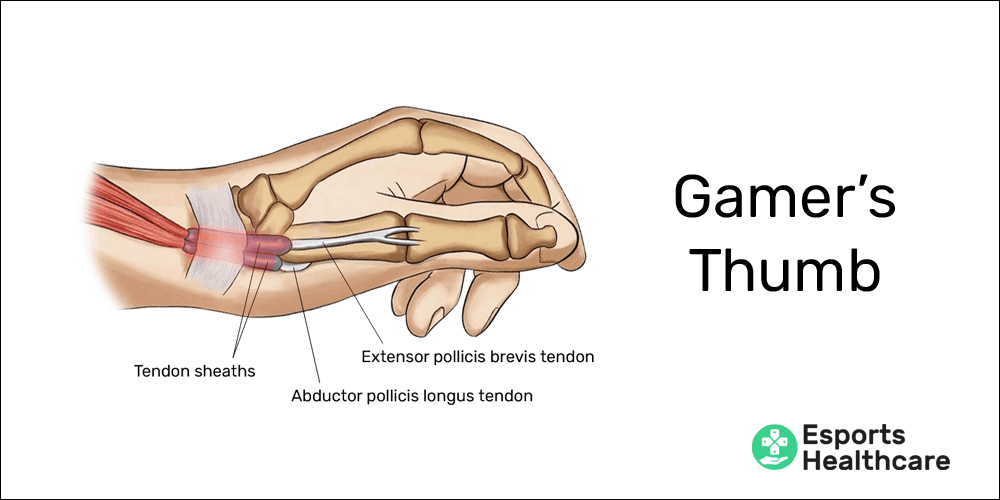
Gamer’s thumb is the common term for the diagnosis of tenosynovitis from repetitive use of the thumb. Specifically, gamer’s thumb affects the tendon sheaths of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus muscles. These muscles pull the thumb away from the hand and palm (see Pertinent anatomy).
This condition is also commonly associated with and precedes de Quervain’s—or stenosing tenosynovitis—of the same tendon sheaths named above. This condition is categorized by thickening and hardening of the tendon sheath and will often require surgery.
In console gaming, these motions are primarily involved in thumb stick movements. This condition has also recently been identified with greater prevalence due to text messaging on mobile devices and is sometimes called “texter’s thumb.” Although possible, a diagnosis of gamer’s thumb is less common for PC gamers than it is for console gamers.
Pertinent anatomy of the thumb
It’s important to know some basic anatomy of the thumb to really understand gamer’s thumb.
In areas of your body where greater-than-normal friction exists, tendons will have a sheath to protect them from damage. The tendon sheaths affected in gamer’s thumb surround tendons that attach from your forearm to your thumb. If you open your hand wide, you can see the tendons pop up on the thumb side of your wrist:
- Extensor pollicis brevis: extension of your thumb (as in opening your hand wide)
- Abductor pollicis longus: abduction of your thumb (pulling away from your palm)
Tendons and tendon sheaths
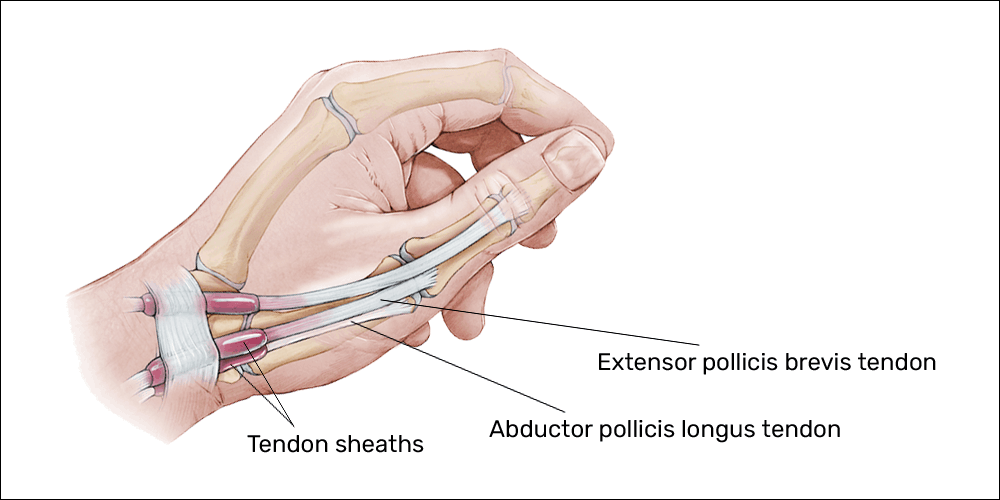
Tendons are bands of fascia that transmit force from muscle to bone. They are continuous with the muscles and bones to which they are attached.
In some areas of your body, tendons may run through anatomical tunnels made of other types of tissue. In other instances, tendons navigate areas of the body with bony projections. In either case, the tendon may be at risk for greater-than-normal levels of friction.
Your body’s protective mechanism for this potential increase in friction is a sheath, or a protecting layer of tissue filled with synovial fluid (lubrication for joints and tendons). The synovial sheath effectively decreases friction by allowing a smooth gliding of the tendon in these areas (think motor oil in the engine of your car to prevent overheating and excessive wearing on the engine).
Tendon sheaths are common in the hands and feet. As previously mentioned, the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons have this protective sheath along the thumb side of your forearm.
Pathophysiology
This injury is in the category of tenosynovitis, which is different from both tendinitis and tendinopathy (ailments of the tendon structure, itself vs. the tendon’s protective sheath). The name tenosynovitis perfectly describes the ailment:
- Teno-: identifying the presence of a tendon
- Synov-: identifying, more specifically, the involvement of the tendon’s synovial sheath
- -itis: identifying that this is an inflammatory condition
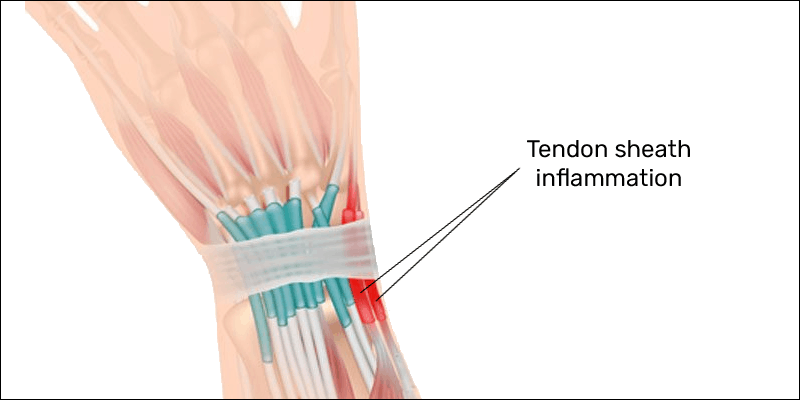
Gamer’s thumb is an inflammatory ailment; however, it is not an inflammation of the tendons! Rather, it is an inflammation of the sheath that surrounds the tendons. This distinction is important because treatment protocols may vary.
A tenosynovitis of any tendon sheath may be caused by direct trauma; however, the absence of trauma would indicate an overuse syndrome. In other words, excessive activation of the thumb muscles and tendons may lead to inflammation of the tendon sheaths and cause symptoms.
In other ailments often named in the category of “overuse” (such as mouse elbow), there is no inflammation. In those ailments, the issue is an imbalance in muscle activity leading to tendon fiber adhesion. In gamer’s thumb, an overuse tenosynovitis, the issue is truly overuse—excessive, high volume activity.
Signs and symptoms of Gamer’s Thumb
If you’re affected by gamer’s thumb, you’re likely to experience the following symptoms:
- Pain: most often, you will experience pain on the thumb side of your forearm and wrist
- Weakness: gripping may feel weak; however, your perceived weakness is more likely due to pain rather than true muscle weakness
Other common findings may include:
- More pronounced symptoms when extending or abducting your thumb (the actions of pulling your thumb away from your hand)
- Bending your wrist to the pinky side of your hand may also increase pain
- Worsening symptoms after periods of activity (playing video games or texting)
- Relief or improvement of symptoms after periods of rest

Gamer’s thumb inflammation
Gamer’s thumb is inflammatory in nature. Inflammation is commonly categorized by pain with accompanying swelling of the area in question, redness of the skin, and heat (feeling warm to the touch). These symptoms may appear but will likely be mild.
If you have a fever, or if you notice moderate-to-severe swelling and significant redness and/or heat, you may be experiencing another, more serious issue. Consult your doctor if you experience these symptoms.
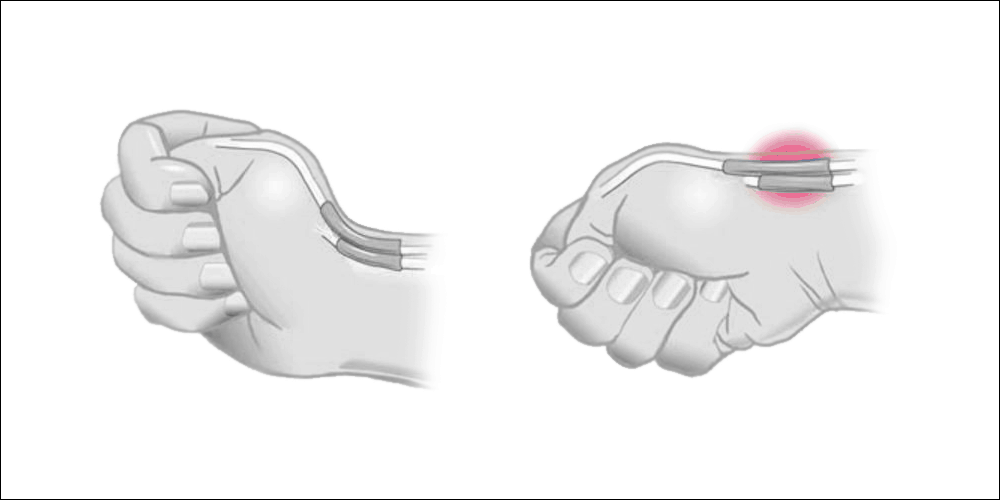
Finkelstein’s test
Finkelstein’s test is an orthopedic maneuver to aid in the diagnosis of gamer’s thumb and/or de Quervain’s (stenosing tenosynovitis). To perform this test, the patient grips their thumb in the palm of their hand. With the thumb gripped in the palm, the patient bends their wrist to the pinky side of their hand.
A positive test is one that results in sharp pain along the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons on the thumb side of the wrist and forearm.
Common mechanism(s) of injury
Gamer’s thumb is more common for console gamers due to the use of the thumb sticks. Common risks for console gamers include:
- Poor hand position
- Gaming with your wrists in ulnar or radial deviation (*read below) may increase the friction of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons underneath the tendon sheath
- *Radial deviation is the term for bending your wrist towards the thumb side
- *Ulnar deviation is the term for bending your wrist towards the pinky side
- Gaming with your wrists in ulnar or radial deviation (*read below) may increase the friction of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons underneath the tendon sheath
- Skipping your warm-up
- The purpose of a warm-up is to increase blood flow to muscles and to lubricate joints and other structures (e.g., tendon sheaths)
- Gaming without first performing a proper warm-up may allow for increased friction of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons underneath their tendon sheaths
- Skipping your cool down
- One important purpose of a cool down is to decrease inflammation
- Gaming without performing a proper cool down afterwards may allow for chronic inflammation of the tendon sheaths

Preventing gamer’s thumb
The most common mechanism of injury for gamer’s thumb is overuse—exacerbated by poor wrist position—and chronic inflammation.
For all hand and wrist injuries, we’ve created a comprehensive injury prevention program. Performing this exercise routine may help reduce your risk for all gamer injuries, including gamer’s thumb.
Hand and wrist position
It is important to keep your wrists neutral! Radial deviation (bending your wrists towards your thumb) and ulnar deviation (bending your wrists towards your pinky) both increase the risk of developing gamer’s thumb.
Use and overuse
- Take breaks to avoid overuse
- Be sure to warm-up your hands and wrists prior to gaming
- Perform the proper stretches when you’re done with your sessions
Risk of progression: stenosing tenosynovitis
An unresolved or improperly treated tenosynovitis may lead to stenosing tenosynovitis, also known as trigger finger. Trigger finger is an irreversible locking of the tendon where you will be unable to extend the finger. This condition most often requires surgical intervention!
If you feel you are experiencing gamer’s thumb or any other tenosynovitis based on the information provided on this page, we urge you speak with your doctor!
Rehabilitation
To effectively resolve gamer’s thumb, it is important to first identify and correct the initial cause. For example, if you’re not taking breaks or you’re gaming with your wrists held in radial or ulnar deviation (described above), protocols may be ineffective because of the constant exacerbation.

Perform a proper warm-up
First, recognize that a proper warm-up is absolutely essential—not only to prevent pain and injury but also to improve your gaming performance. Our warm-up routine is comprehensive to include all muscles and joints involved in your gaming sessions.
Take breaks while gaming
Do yourself a favor, and take breaks between matches. Additionally, schedule longer (10-minute) breaks intermittently during long hours of gaming.
If you’ve read through our page outlining habits healthy gaming, you’ll know that stretching is important but not until your entire session is over. DO NOT stretch your muscles during intermittent breaks!
To stay loose during your sessions, repeat some of the exercises and movements in the warm-up. Stretching mid-session may decrease your performance and will not effectively aid in injury prevention.
Make healthy diet choices
Do not underestimate the absolutely invaluable aspect of nutrition. Eating unhealthy foods or consuming unhealthy beverages will simply make your body unhealthy. Check out our page describing our favorite healthy gamer snacks for better snack options during your gaming sessions.
Also, drink plenty of water. Generally, the recommendation for fluid intake is half your body weight (measured in pounds) in fluid ounces per day. So, if you weigh 120lbs, you should drink 60 fl. oz. If you weigh 160lbs, you should drink 80 fl. oz, and so on.
Rest and recovery
We will never tell you to stop gaming. However, your rest and recovery are important. Taking beaks between games and matches is part of that, but your recovery after and between these long sessions is even more important.
Post-session stretching
When you’re done gaming, and you won’t be gaming again until tomorrow or later, it is time to stretch! We have a stretch routine to assist in the prevention of aches, pains, and injuries that gamers may face. Following physical activity, stretching may increase range of motion and release chronic tension in muscles.
The unmatched importance of sleep
In life, there is not one single thing more valuable to your health than your sleep. Please, read our post on sleep to better understand its importance. And, for the sake of your health, schedule and commit to a regular sleep schedule including eight hours of uninterrupted sleep!
Contrast therapy
For treatment of gamer’s thumb, we suggest contrast therapy. Begin with heat on the area for ~10-15 minutes. Following the heat, replace it with ~10-15 minutes of ice or cold therapy. Contrast therapy will open the blood vessels to help eliminate toxins followed by clamping the blood vessels and preventing excess inflammation.
Other anti-inflammatory measures
As chiropractors and providers who are not established as your doctor, we cannot (legally) recommend anti-inflammatory medication. However, if inflammation exists (pain with redness, swelling, and heat), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen (Aleve), aspirin, or acetaminophen (Tylenol) may be useful.
If you’re interested in taking NSAIDs or any other medication, our official advice is that you must first speak with your doctor.
Corticosteroid injections
If conservative therapies are not improving the condition, the next step would be to consider corticosteroid injections to eliminate chronic inflammation and to prevent stenosing tenosynovitis and the need for surgery. These injections are widely used and successful in preventing the need for surgery for gamer’s thumb.
Injections are considered minimally invasive (as opposed to the more invasive procedures of surgery) because they include puncturing the skin and tendon sheath to deliver the medication.
Splinting and bracing
There are few occasions where immobilizing a bodily structure is appropriate, and gamer’s thumb is one of those occasions. Due to the inflammatory nature of the condition caused by movement, reducing movement is valuable.
A thumb stabilizer splint or brace is an excellent choice to immobilize your thumb to allow healing. Combining immobilization with previously mentioned therapies may help to alleviate and resolve symptoms of gamer’s thumb.
When using a splint or brace, the timing is also extremely important. For rehabilitation of gamer’s thumb, we recommend wearing a splint or brace on your down time prior to and following your gaming sessions. If you have pain overnight and/or wake up with pain, it may also be wise to wear the brace while sleeping.
