Mouse elbow: a devastating injury for PC gamers
Key points
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor. Esports Healthcare disclaims any liability for the decisions you make based on this information.
The information contained on this website does not establish, nor does it imply, doctor-patient relationship. Esports Healthcare does not offer this information for diagnostic purposes. A diagnosis must not be assumed based on the information provided.
What is mouse elbow?
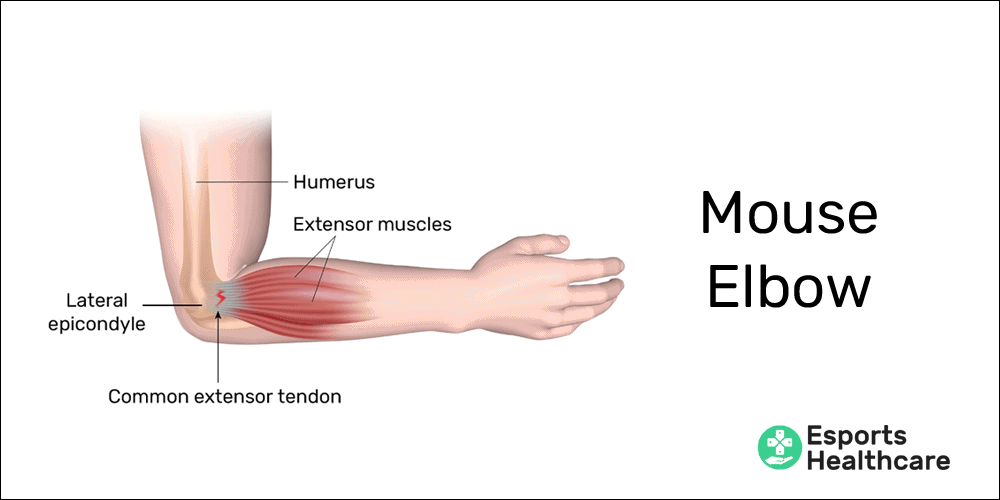
Mouse elbow is an ailment that occurs in the extensor tendons of the forearm (which control the wrist and fingers) that attach to the outside (thumb side) of the elbow. The muscles involved are the extensor muscles that open the hand and bend back the wrist. As the name suggests, PC gamers are more likely to experience this injury due to the use of the mouse.
Due to misuse and imbalance, the fiber orientation of the extensor tendons on the outside of the elbow become disrupted. This dysfunction is called a tendinopathy, which is different than tendinitis—a common misnomer for this condition. We discuss this difference in more detail in the Pathophysiology section below.
Pertinent anatomy
It’s important to know some basic anatomy of the fingers, hand, wrist, and forearm to understand mouse elbow.
To begin, the tendons affected in mouse elbow are collectively called the common extensor tendon. This tendon is made up of 4 individual muscles and tendons that converge in one spot—a projection on the outside of the humerus (upper arm bone) called the lateral epicondyle:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis: extension (bending backwards) and radial deviation (bending towards your thumb) of your wrist
- Extensor digitorum: extension of your wrist and 4 fingers
- Extensor digiti minimi: extension of your wrist and pinky finger
- Extensor carpi ulnaris: extension and ulnar deviation (bending towards your pinky) of your wrist
One additional muscle which may be involved attaches just above the common extensor tendon onto a bony prominence called the supracondylar ridge of the humerus.
- Extensor carpi radialis longus: extension and radial deviation of your wrist
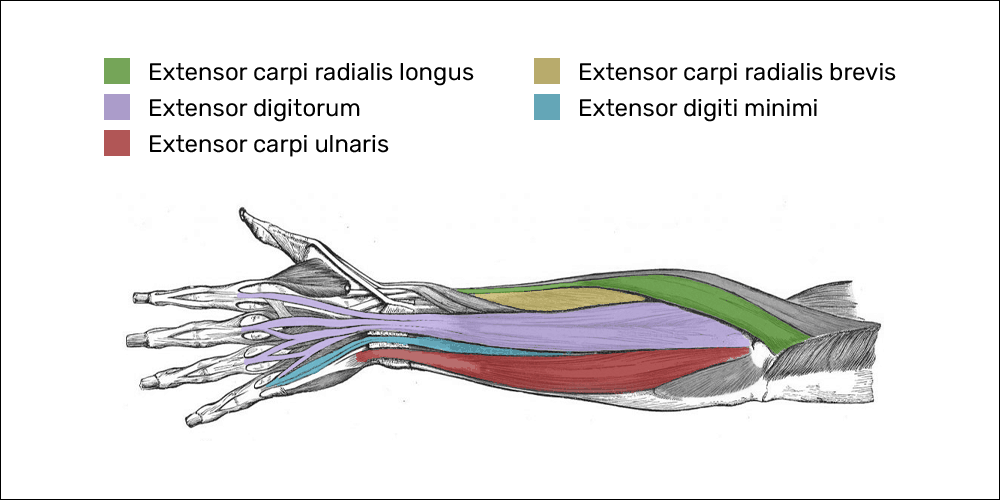
On their distal ends (further away from the center of the body), each of these muscles attach to different parts of the hands or fingers, but mouse elbow tendinopathy occurs in the attachment at the elbow.
Pathophysiology
This injury is a tendinopathy! It is NOT inflammatory in nature, and so the term tendinitis is not appropriate! This is critical to determine the appropriate prevention and rehabilitation.
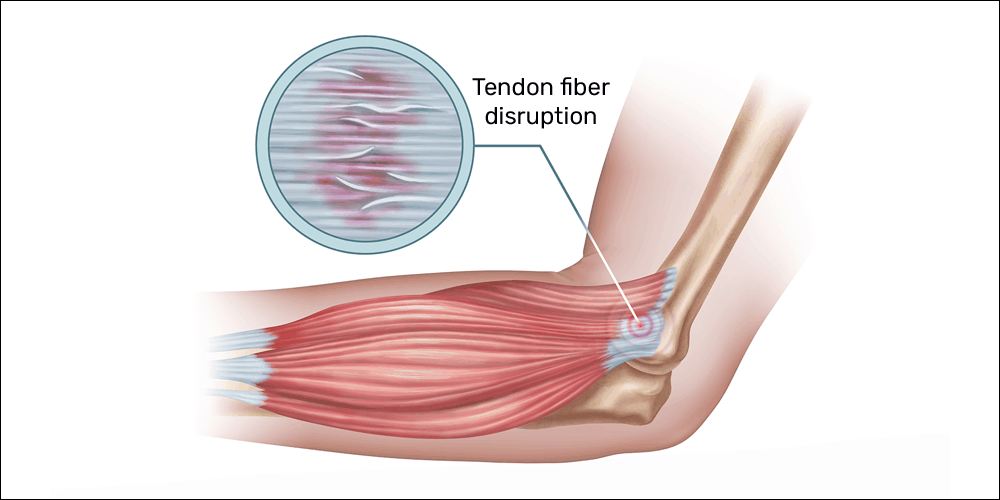
Mouse elbow occurs when there is at least one of two imbalances in muscle contraction. If one or both of these imbalances occur over time, degeneration of collagen (the protein found in connective tissue) occurs. This leads to the disruption of the tendon fiber orientation in the common extensor tendon.
The strong fibers of a tendon should line up parallel with one another. In tendinopathy, these fibers will become jumbled or disorganized—commonly described as adhesion formation—causing pain and affecting the movement of the tendon and the elbow joint.
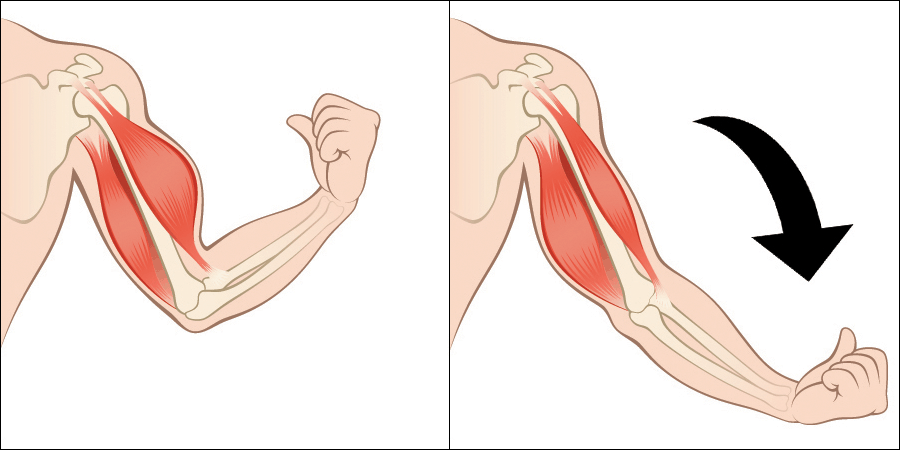
- Concentric vs. eccentric imbalance
- Concentric: the shortening phase of a muscle contraction
- PC gamers: lifting the fingers off the mouse is a concentric contraction; lifting the fingers requires more force than striking the keys or mouse buttons
- Weight lifting example: the up-phase of a biceps curl (raising the dumbbell up to your shoulder)
- Eccentric: the lengthening phase of a muscle contraction
- In gaming, there is no instance of an appropriate eccentric contraction, and this is the problem!
- Weight lifting example: the down-phase of a biceps curl (controlled lowering of a dumbbell back to your hip)
- Concentric: the shortening phase of a muscle contraction
- Agonist vs. antagonist imbalance
- Agonist: the active muscle during a particular movement
- PC gamers: the agonist tends to be the extensor muscles; lifting the fingers off the keyboard and mouse is a resisted movement (against gravity), where tapping keys and mouse buttons requires little muscle activation
- Antagonist: the muscle that opposes the agonist; this muscle (or group of muscles) will be relaxed during agonist contraction
- PC gamers: the antagonist muscles are the flexor muscles of the wrist and hand (e.g., making a fist); these muscles are not challenged with any significant resistance during PC gaming
- Agonist: the active muscle during a particular movement
For console gamers, these imbalances are not pertinent for mouse elbow. These imbalances in console gaming are more likely to lead to medial epicondylosis or gamer’s thumb.
Concentric vs. eccentric imbalance
When concentric contractions occur too frequently without the counterbalance of eccentric contraction, collagen begins to degenerate from the chronic shortening. Eccentric contraction—the lengthening of a muscle and tendon under tension—helps maintain the tendon fiber orientation.
Mechanical loading, particularly in the eccentric phase, protects tendons from injury!
Agonist vs. antagonist imbalance
When agonist muscle actions occur too frequently without the counterbalance of their antagonist, there is imbalance in the strength and tension on the joints involved. When strength and tension are not balanced, the muscles can be overworked and injury becomes more common.
The concentric vs. eccentric imbalance is usually the direct cause of any tendinopathy, but the agonist vs. antagonist imbalance may exacerbate the ailment and prolong healing time.
Signs and symptoms
If you’re affected by mouse elbow, you’re likely to experience the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Most often, you will experience pain at the outer portion of your elbow with wrist movements and gripping
- Bending your wrist and fingers back may cause pain by contracting the extensor muscles
- Flexing your wrist and fingers forward may cause pain by stretching the extensor muscles
- Weakness
- Gripping may feel weak; however, your perceived weakness is more likely due to pain rather than true muscle weakness

Other common findings may include:
- More pronounced symptoms with extension of your wrist(s) (e.g., using a mouse or keyboard)
- Worsening symptoms following periods of rest
- Relief or improvement of symptoms after warming up the extensor muscles
Note: mouse elbow is considered a tendinopathy, and inflammation will not be present. Inflammation is categorized by pain with accompanying swelling, redness, and heat (feeling warm to the touch).
If you notice these signs of inflammation, you are experiencing something different than simple mouse elbow tendinopathy. You should consult your doctor if you are concerned about these symptoms.
Common mechanism(s) of injury
For gamers, mouse elbow is more common for PC users due to the position and action of the wrists and hands using a keyboard and mouse. Common risks for PC users include:
- Poor hand position
- Allowing excessive extension of your wrists over the keyboard and/or mouse will create over-activation and shortening of the common extensor muscles and tendons
- Allowing excessive ulnar deviation (bending of your wrist towards the pinky side) may lead to aggravation of the extensor carpi ulnaris muscle, specifically
- Lack of eccentric contraction
- As described in Pathophysiology above, the actions performed in PC gaming do not include eccentric contraction, or lengthening of the extensor muscles
- The imbalance of muscle shortening without lengthening under tension leads to tendon fiber disruption
- Lack of antagonist muscle contraction
- Also described in Pathophysiology above, lifting your fingers off the keyboard and mouse is a more aggressive activity; pressing keys and mouse buttons down is not a strong muscle activity
- The lack of forceful flexor muscle contraction allows for over-activity of the extensor muscles, perpetuating the shortening and fiber disruption of the tendons at the elbow

Prevention
The most common mechanisms of injury for mouse elbow are imbalances—both in movement and in body positioning (posture and ergonomics). Therefore, correcting your posture and balancing both muscle contraction and activation are simple, yet extremely effective preventative measures.
For all common gamer injuries of the fingers, hands, wrists, and forearms—including mouse elbow—we’ve created a comprehensive injury prevention program. Performing this exercise routine may help reduce your risk.
Eccentric muscle contraction
The lengthening phase of muscle contraction is the most important! Below, we have a list of exercises that may help resolve this ailment. It is absolutely essential to perform the eccentric, or “down-phase” portion of these exercises slowly and under control!
In addition to these mouse elbow-specific preventative measures:
- Take breaks to avoid overuse
- Be sure to warm-up your hands and wrists prior to gaming
- Perform the proper stretches when you’re done with your sessions
From our injury prevention video, the exercises and stretches are:
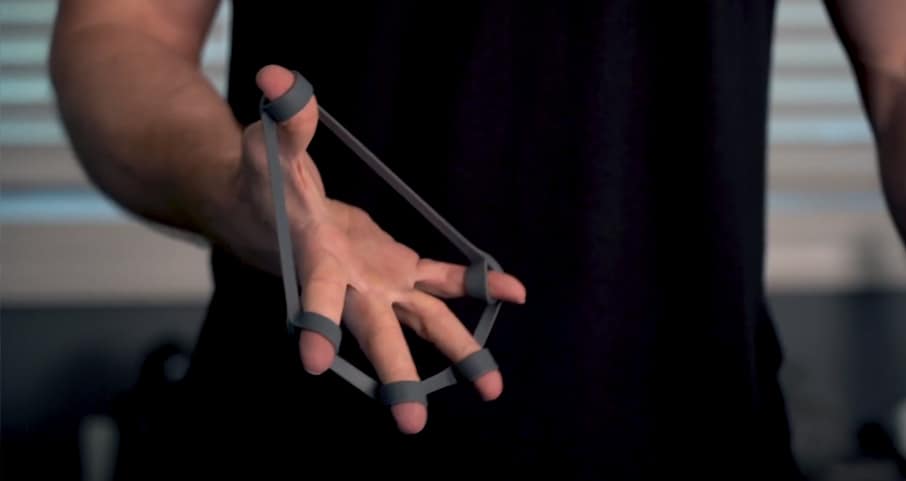
Resisted finger extension
- Set up the finger band around the tips of your fingers, including your thumb
- Begin with your finger pads together. Then, open your hand as wide as you can
- SLOWLY, and under control, return to the starting position
- Repeat steps 2-3 for a total of fifteen (15) repetitions

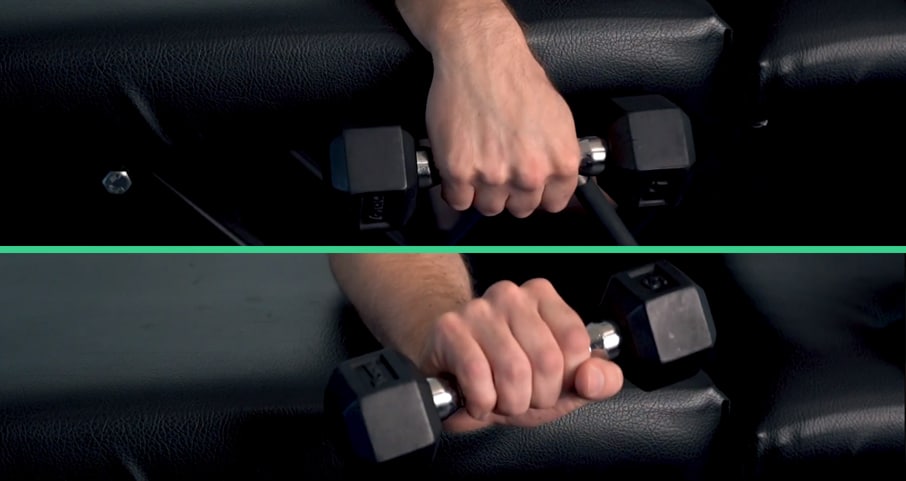
Weighted wrist extension
- Lay your forearm down on a flat surface with your palm facing downward
- Grab a dumbbell or other small, weighted object, and let your wrist hang over the edge; extend the dumbbell upward
- SLOWLY, and under control, return to the low, hanging position
- Repeat steps 2-3 for a total of fifteen (15) repetitions
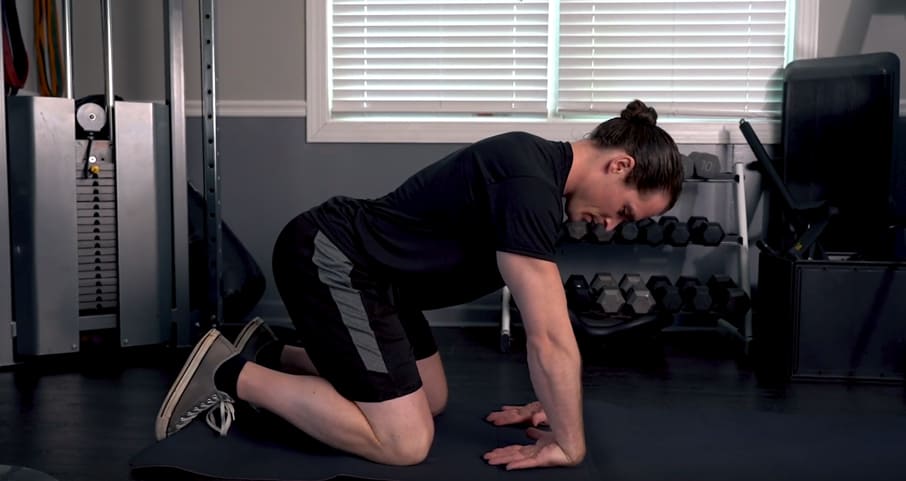
Post-facilitation stretch, wrist extensors
- Flex your wrists as far as you can, and place them on the ground
- For 10 seconds, press your hands into the ground as hard as you can
- After 10 seconds, try to lift your hands and fingers off the ground
- At the same time, lean backwards to stretch the extensor muscles of your forearms
- Repeat steps 1-4 for a total of three (3) sets

Agonist vs. antagonist muscle activity
Balancing the muscle activity at any joint will help keep muscles healthy. For PC gamers, extension of the wrist and fingers is the strenuous action; therefore, it is important to perform flexion exercises and stretches for the wrists and fingers for balance.
On our injury prevention video, these exercises and stretches are:
Weighted wrist curl
- Lay your forearm down on a flat surface with your palm facing upward
- Grab a dumbbell or other small, weighted object, and let your wrist hang over the edge
- Curl the dumbbell upward, and return to the low, hanging position
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for a total of fifteen (15) repetitions
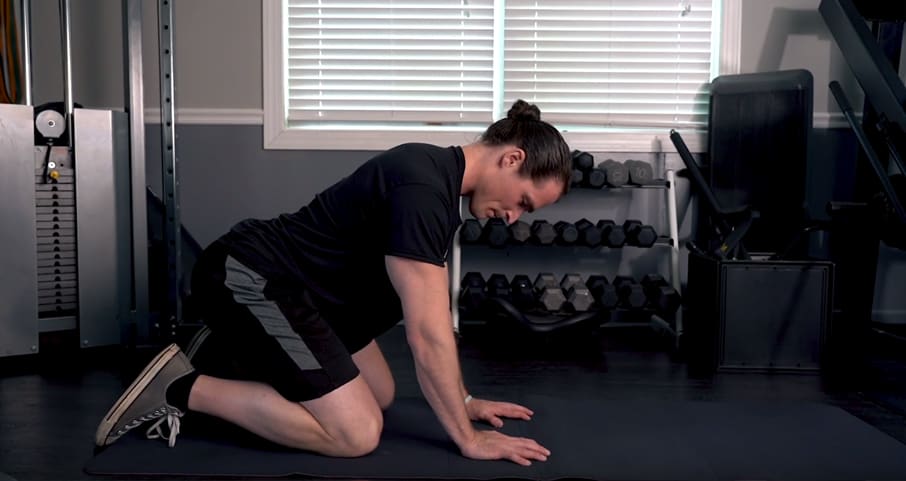
Post-facilitation stretch, wrist flexors
- Extend your wrists as far as you can, and place them on the ground.
- For 10 seconds, press your hands into the ground as hard as you can.
- After 10 seconds, try to lift your hands and fingers off the ground.
- At the same time, lean forward to stretch the flexor muscles of your forearms.
- Repeat steps 1-4 for a total of three (3) sets.

Rehabilitation
To effectively resolve mouse elbow, it is important to first identify and correct the initial cause. For example, if your body is in poor position while gaming or you’re not performing the eccentric action of the extensor muscles outside of gaming, protocols may be ineffective because of the constant exacerbation.
Step 1: aggressive cross-friction massage
The provider should use a firm surface (thumb pressure or a knuckle, for example) to apply moderate pressure to the common extensor tendon and scrape perpendicularly across the tendon. Unfortunately, this maneuver tends to be moderately painful.
This will loosen the tendon matrix and make it more malleable for the next part of the treatment.
Step 2: Hypervolt+®
In multiple case reports in practice, Esports Healthcare has found that the use of the Hypervolt+® percussion tool following cross friction and preceding heavy eccentric loading has allowed for more rapid recovery.
To your tolerance, the Hypervolt+® can be used to massage the extensor muscles and tendons on the the forearm (at the elbow).
When compared to their muscles, tendons have approximately 7.5x less oxygen consumption due to limited blood flow, and this is one reason why tendons heal more slowly.
In order for your body to heal any tissue, blood is required to remove toxins and cellular waste, to bring oxygen into the working cells, and to provide nutrients (in other words, building materials) to the damaged tissue.
The Hypervolt+® tool was added at this step to stimulate all the soft tissue in the region of the affected tendon to increase blood flow. With increased blood flow comes increased oxygen and nutrients to enhance healing; there will also be more rapid removal of toxins from the healing process.
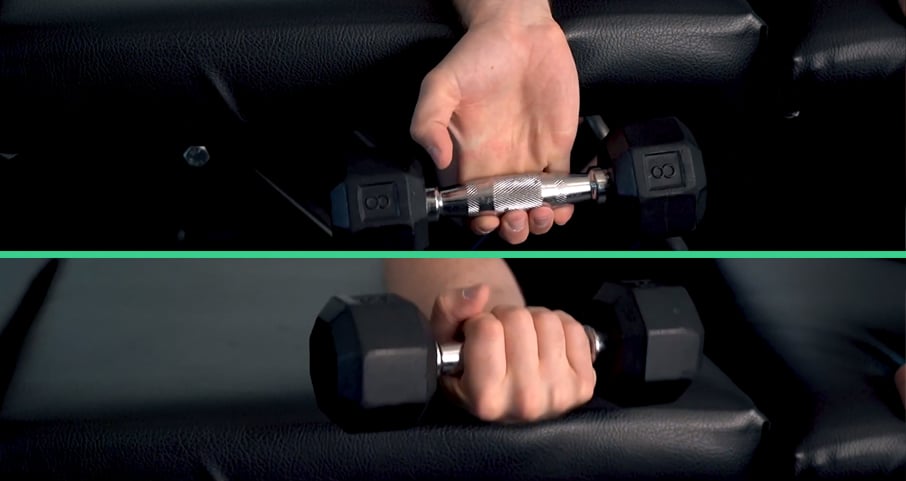
Step 3: heavy eccentric loading
Following cross-friction to loosen the tendon matrix, resistance must be added to lengthen the tendon under tension. This resistance should be moderate-to-significantly heavy in order to properly pull the tendon fibers taut.
For mouse elbow, this would involve holding a weight (dumbbell or other small, weighted object) in the palm of the hand with the wrist extended and elbow flexed (see image below). In a slow, controlled manner, allow the elbow to open and wrist to drop—pulling the tendon.
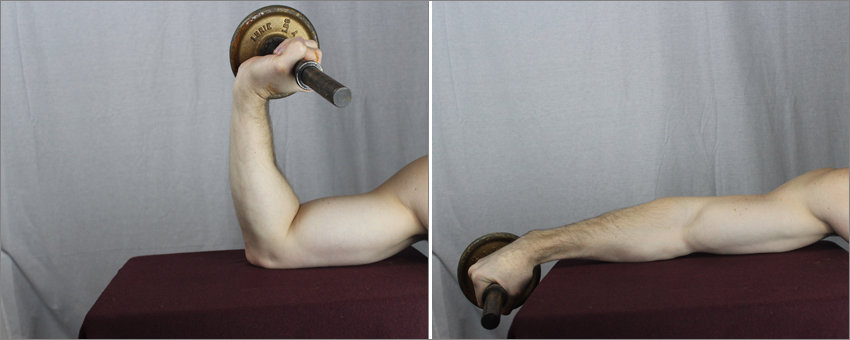
Step 4: continued blood perfusion via heat therapy
Using heat packs or other heat therapies (e.g., infrared laser) on the affected area should conclude this protocol. Generally, a heat pack should be used for 10-15 minutes. Adding a damp towel between the heat pack and the affected area will increase its effectiveness by creating moisture that penetrates further into the body.
Generally, people think to ice their ailments to relieve the pain. However, ice relieves inflammation, and as previously discussed, inflammation is not the cause of pain. Therefore, ice would not help this condition. In fact, icing the affected area may prolong the healing process.
For a tendinopathy, heat is more helpful than ice. Following resolution, continuation of these protocols allows for prevention of this condition from reoccurring.
